“How much should I weigh?” is most likely a question for which many people are seeking for an answer. However, there is no specific ideal weight for each person since, in addition to mass, a variety of other factors, such as age, body fat ratio, height, gender and body fat distribution, or body shape, all play a part in determining a healthy weight. Even if there is no ideal weight, everyone should set a healthy weight point and maintain it. Allow Illume to walk you through all of the methods for effective weight management and tips for maintaining a healthy weight.
About Weight Management
Many people, especially women, must be asking themselves the same question: am I okay with this weight, whether it is fat, skinny, or normal, and how much more weight I should gain or lose? This, however, cannot be determined only by weight. For children under the age of five, it is important to evaluate criteria such as weight for age, height for age, and height for weight to assess their nutritional health.
Obesity, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular problems can all be increased by being overweight. It is not entirely accurate that people who are overweight can cause health concerns. However, the researchers believe that, while these extra pounds may not have an immediate impact on a person’s health, a lack of control may cause problems in the future.
So what methods and tips are there to help track and control our weight? Let’s find out.
Methods for weight management
a) Body Mass Index (BMI):
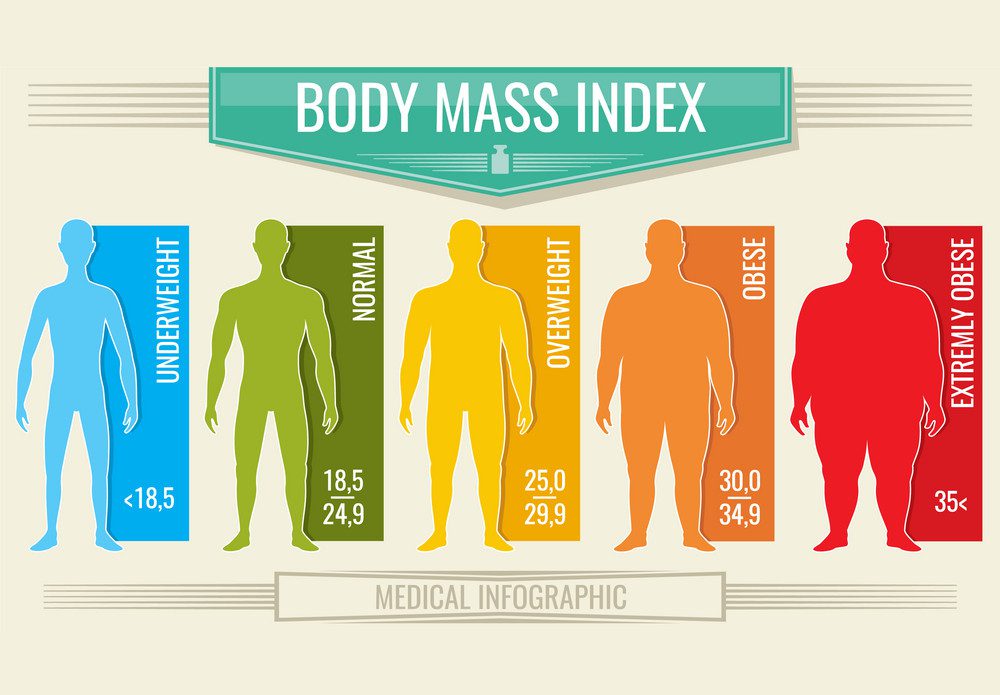
Body mass index (BMI) is a popular method for determining a person’s ideal body weight. BMI calculates a person’s weight in relation to their height.
BMI-based formula for calculating ideal weight:
BMI = Weight / [(Height)x2]
(Height is measured in meters, while weight is measured in kilograms)
- NOTE: BMI does not apply to pregnant women, athletes, or bodybuilders.
According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH):
- BMI < 18.5: Underweight
- 5 ≤ BMI ≤ 24.9: Healthy / Ideal
- 25 ≤ BMI ≤9: Overweight
- 30 ≤ BMI ≤9: Obese.
- BMI > 35: Extremely obese
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple measurement. Although this measurement takes height into consideration, it excludes variables such as:
- Waist or hip measurements
- The distribution or percentage of fat
- Muscle mass ratio
These can have an impact on one’s health as well.
High-performance athletes, for example, are often fit and have little body fat. They may have a greater BMI due to higher muscle mass, but this does not imply that they are overweight.
BMI may also give a general notion of whether a person’s age-appropriate weight is healthy, and it can be used to track trends in research. However, it is not the only measurement that can be used to determine whether or not a person’s weight is healthy.
b) Waist-to-hip ratio (WHR)
The waist-to-hip ratio compares a person’s waist size to their hip size. According to research, people who have a lot of body fat around their midsection are more prone to acquire cardiovascular disease (CVD) and diabetes. The higher the waist measurement in proportion to the hips, the greater the risk.
As a result, the waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) is a useful tool for determining if a person is an appropriate weight and size.
How to Calculate Waist-to-Hip Ratio:
- Measure around the waist at its narrowest point, which is generally slightly above the navel.
- Divide the waist circumference by the circumference of your hips at their fullest point.
Men and women have distinct body shapes, thus how WHR impacts CVD risk differs. The following research suggests that WHR may impact the risk of cardiovascular disease:
In men:
- Below 0.95: The risk of heart disease is low
- From 0.96 to 1.0: Moderate risk
- From 1.1 and above: High risk
In women:
- Below 0.80: Low risk
- From 0.81 to 0.85: Moderate risk
- From 0.86 and above: High risk
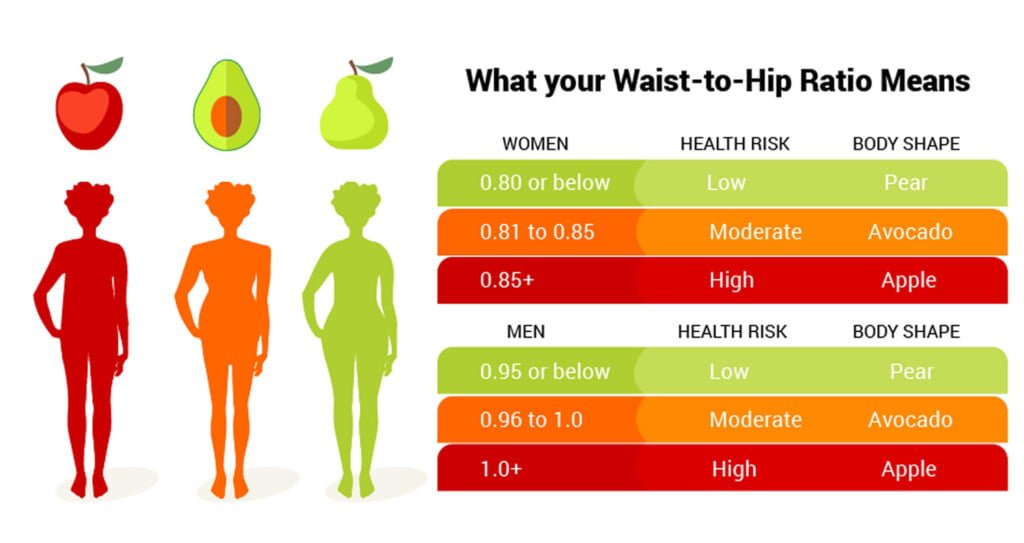
These numbers, however, may fluctuate depending on the source and population to whom they apply. WHR may be a stronger predictor of heart attacks and other health problems than BMI, which does not take fat distribution into consideration.
A 2013 research of 1,349 people’s health records from 11 nations discovered that individuals with a greater WHR had an increased risk of medical and surgical problems connected with colorectal surgery. WHR, on the other hand, does not accurately assess a person’s percentage of total body fat or muscle-to-fat ratio.
c) Waist-to-height ratio (WtHR)
Waist-to-height ratio (WtHR) is another tool that can more accurately predict heart disease risk, diabetes, and overall mortality than BMI. A person with a waist measurement that is less than half their height is less likely to develop some life-threatening health problems.
How to Calculate Waist-to-Height Ratio: WtHR is calculated by dividing a person’s waist size by their height. If the result is 0.5 or less, they have a healthy weight.
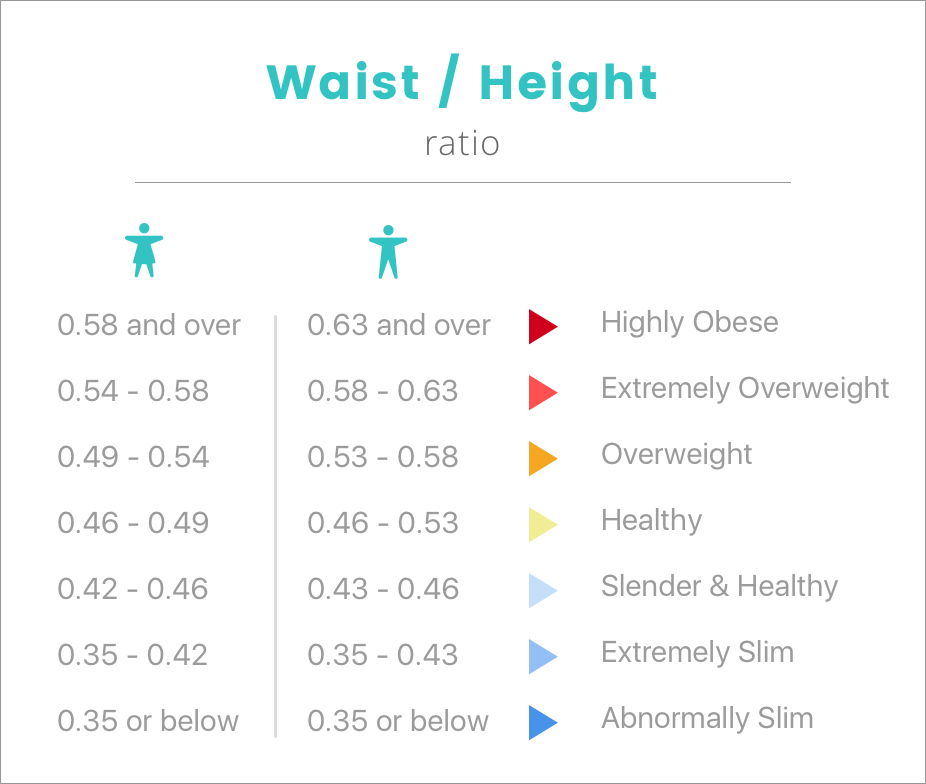
A woman who is 163 cm tall, for example, must have a waist measurement of less than 81 cm. A man who is 183 cm tall must have a waist measurement of less than 91 cm. These measurements result in a waist-to-height ratio (WtHR) of approximately under 0.5.
In a study published in the journal Plos One, researchers concluded that WtHR was a better predictor of mortality than BMI. The authors also mention findings from another study, which included data from around 300,000 people from various backgrounds, and concluded that WHtR was better than BMI for predicting heart attack, stroke, diabetes, and high blood pressure. As a result, WHtR is regarded as a helpful screening tool.
Waist size measurements can be a useful predictor of a person’s health risk since fat buildup in this area can be detrimental to internal organs such as: heart, kidneys, and liver.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention notes that men with a waist circumference of 101cm or more, or women with a waist circumference of 89cm or more, are at a higher risk than others:
- Diabetes type 2
- High Blood Pressure
- Coronary artery disease
d) Body fat percentage
Body fat percentage is calculated by dividing a person’s fat weight by their overall weight. Total body fat includes both essential fat and stored fat.
- Essential Fats: In order to exist, a person need essential fats, which are involved in a range of biological activities. For men, essential fats should account for between 2 and 4% of the body weight. For women, that number is 10 to 13 %, according to the American Council on Exercise.
- Stored fat: Fat tissue protects the internal organs in the chest and abdomen, and the body can use it for energy if needed.
In addition to general standards for men and women, the ideal total fat percentage might vary depending on a person’s body type or activity level.
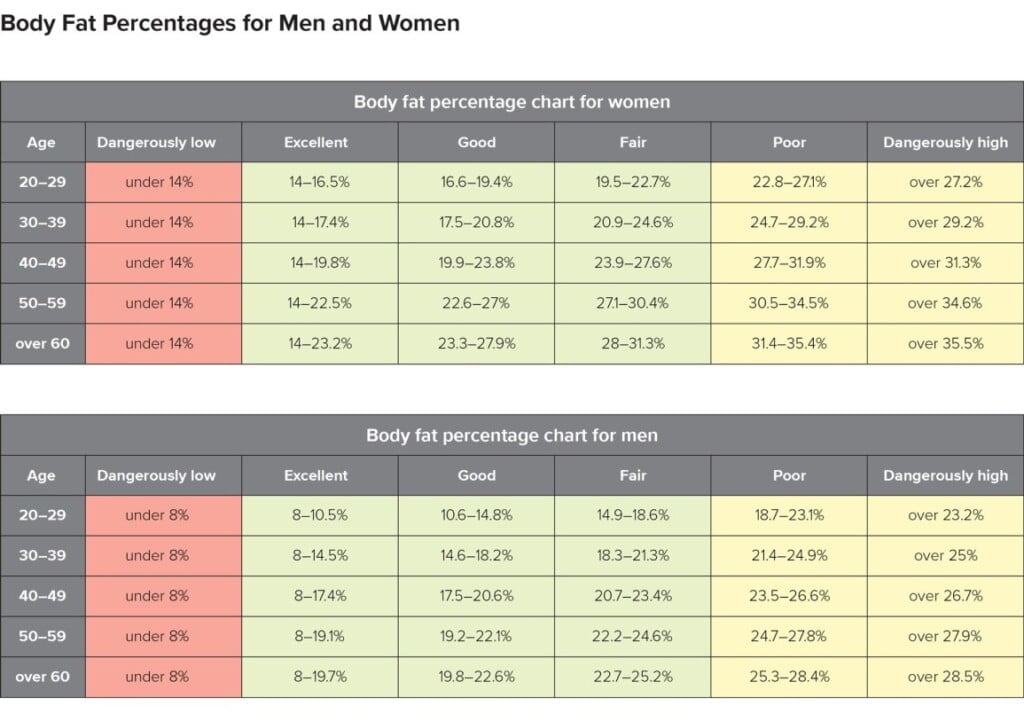
The following rates are recommended by the American Council on Exercise:
- Athletes: 6–13% (male); 14–20% (female)
- Suitable for non-athletes: 14–17% (male); 21–24% (female)
- Medium: 18–25% (male); 25–31% (female)
- Overweight: 26–37% (male); 32–41% (female)
- Obesity: 38% or more (male); 42% or more (female)
A high body fat percentage may indicate a risk of:
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- High Blood Pressure
- Stroke
Calculating body fat percentage can be a good way to measure a person’s fitness level because it reflects the person’s overall health. Body mass index (BMI), on the other hand, does not distinguish between fat and muscle mass.
Tips for maintaining a healthy weight
To maintain a healthy weight, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, which includes nutrition, exercise, and other living habits.
Take the following steps if you are overweight and need to lose weight:
- Try eating nutritious meals that consist mostly of healthy food such as fruits and vegetables, lean protein, whole grains, nuts, and so on.
- Get 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise each week, such as walking, or 75 minutes of high-intensity exercise, such as jogging, each week.
- Maintain a food journal to track calories: in order to lose weight, you must burn more calories than you consume. Use calorie tracking apps on your phone to monitor how many calories you consume each day and make adjustments as needed. It’s very easy to consume more calories than you need without even realizing it if you don’t track them.
- Adopt an active lifestyle: in addition to exercising, be active every day by making little adjustments such as walking more, climbing stairs, doing housework regularly, and so on.
- Get adequate sleep: a lack of sleep on a regular basis increases the risk of weight gain.
- Reduce stress: stress raises levels of the hormone cortisol, which causes overeating and weight gain.

SUMMARY:
There are several methods for determining your healthy weight. However, all of them have limits and are not completely precise, especially when done at home.
Whether you are a healthy weight or overweight, you should eat a healthy diet, exercise routinely, and stay active every day. These not only assist in weight loss and maintaining a healthy weight, but they also provide several health and disease-prevention benefits.
DeBarra Mayo once said “To maintain good health requires good nutrition and a healthy dose of exercise”. We are all responsible for our own bodies. So, Illume does hope you will make the right choice for maintaining your body healthy.

