Yogurt is a healthy and delicious snack. In fact, some countries consider it a staple food. So, join ILLUME eMAG to find out what is so great about yogurt.
How it is made
Regular yogurt made with cow’s milk. The milk gets heated up and mixed with bacteria, particularly Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, then it gets kept warm (43-46°C) for several hours. At that time, the bacteria start to convert the sugar in the milk, lactose, to lactic acid. That thickens the milk and creates the tart flavor.

Since the bacteria broke down some of the lactose, people with lactose intolerance could enjoy some of the yogurts. However, if you are too sensitive, you should have plant-based yogurt instead. Furthermore, people with milk allergies should stay away from yogurt as well, since it still contains casein and whey, the proteins that some people are allergic to.
Yogurt nutrition
Protein

One cup (245 grams) of plain yogurt made from whole milk packs about 8.5 grams of protein, which is impressive. Getting enough protein is important for appetite regulation, as it increases the production of hormones that signal fullness. It may automatically reduce the number of calories you consume overall, which is beneficial for weight control.
Calcium
Just one cup provides 49% of your daily calcium needs. Almost every cell in the body uses calcium in some way, including the nervous system, muscles, and heart. Your body uses calcium to build healthy bones and teeth, keep them strong as you age, send messages through the nervous system, help your blood clot, and make your muscles contract.
Phosphorus
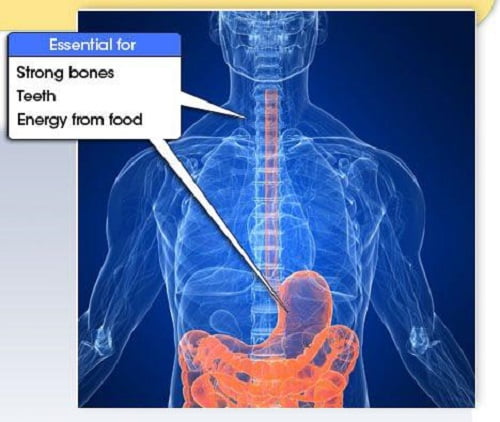
One cup provides 38% of your daily need for phosphorus. Phosphorus plays multiple roles in the body. It is a key element in bones, teeth, and cell membranes. It helps to activate enzymes and keeps blood pH within a normal range. Phosphorus regulates the normal function of nerves and muscles, including the heart, and is also a building block of our genes, as it makes up DNA, RNA, and ATP, the body’s major source of energy.
B vitamins – riboflavin and B12
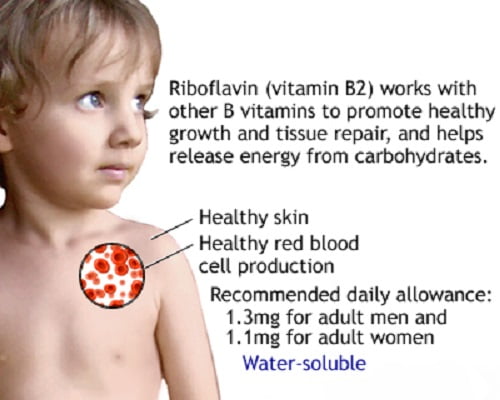
Yogurt is a good source of riboflavin and B12 (only animal base yogurt). Riboflavin is a key component of coenzymes involved in the growth of cells, energy production, and the breakdown of fats, steroids, and medications. Vitamin B12 is needed to form red blood cells and DNA. It is also a key player in the function and development of brain and nerve cells.
Additional information
Much like milk should be avoided when you want to intake more iron, you should do the same for yogurt. This is because calcium inhibits iron absorption. 200 mg of calcium is enough to affect iron absorption in the body. People have not really discovered why this happens, but one of the explanations could be that calcium “competes” with iron for transportation from the digestive tract into the body, since the protein that transports iron into intestinal cells can transport other molecules, too, including calcium.

